A new study in Nature Communications claims COVID vaccines decrease cardiovascular harms. Sadly, the study is not trustworthy.
When scientists fail to report necessary information, trust is lost
A recent paper in Nature Communications is being offered as evidence that COVID vaccines, including boosters, reduce the risk of heart attacks. The paper is flawed, and news organizations and doctor who accept its conclusions at face value are not good at reading medical science. Let’s break it down.
The paper compares rates of 11 cardiovascular outcomes between people who got 1 dose of COVID vaccines, 2 doses (aka the primary series), and additional/ booster doses. Each comparison is to people who got *all but that many doses,* and hazard ratios come from a Cox model— meaning they adjusted for characteristics they could measure (but not one’s they could not)
The first question a scientist would ask is: Hmm, are the people who get 0 doses similar to those who get 1,2, and 3 doses?
The paper shows they are not similar at all. On one coarse metric of societal deprivation, people who unvaccinated are way more deprived than those go got the vaccine. People who are unvaccinated are more likely to smoke.
Even among people who got 2 doses, but did/ or did not get a third. The supplemental tables show fewer people with most deprivation 1-2 got mrna boosters than those who didn’t get boosters at all.
Btw, the index of deprivation is a pretty shitty variable. It lumps anyone in the same color square as the same— whether you live in the best or worst house on the block. Imagine if the researchers actually had the individual household wealth and income among vaccine recipients.
Problem 1: There is likely residual confounding. Healthier, obedient people keep getting doses, and they might have fewer heart attacks not because of dose after dose, but because they are healthier. The authors can’t adjust for what they don’t measure.
A second problem with the paper is that what happens if there is someone named Bob. Bob got 2 doses and is planning to get his booster on Monday. But on Saturday he has chest pain and a heart attack. He can’t get the booster, and automatically his MI gets counted in the *didn’t get a booster group*. This is a type of immortal or guarantee time. People are much less likely to experience events only in the group that got more shots between the time they intend to get the shot and when they get the shot because some of these events really fuck up your plans. I don’t see how the authors seriously address this issue.
Problem 2: There are likely residual time-zero problems/ immortal time.
One way that an outside observer could see if the authors have fixed the confounding and time-zero problem is if the authors provide falsification testing. Bapu Jena, from Harvard, and I explained how and why to do this 11 years ago in JAMA.
Basically, the authors should report the rate of things that boosters could not possible lower, like car accidents or non-covid mortality, if these are also *lowered* by boosters, the study is flawed. Elsewhere we found this was the case for Israeli booster data, which the authors did not make immediately available. All the israeli data was horribly confounded.
But these authors don’t do any of that!
Ultimately, it is shameful that Nature Communications did not demand falsification testing, and very weird that they didn’t ask for covid and all cause mortality.
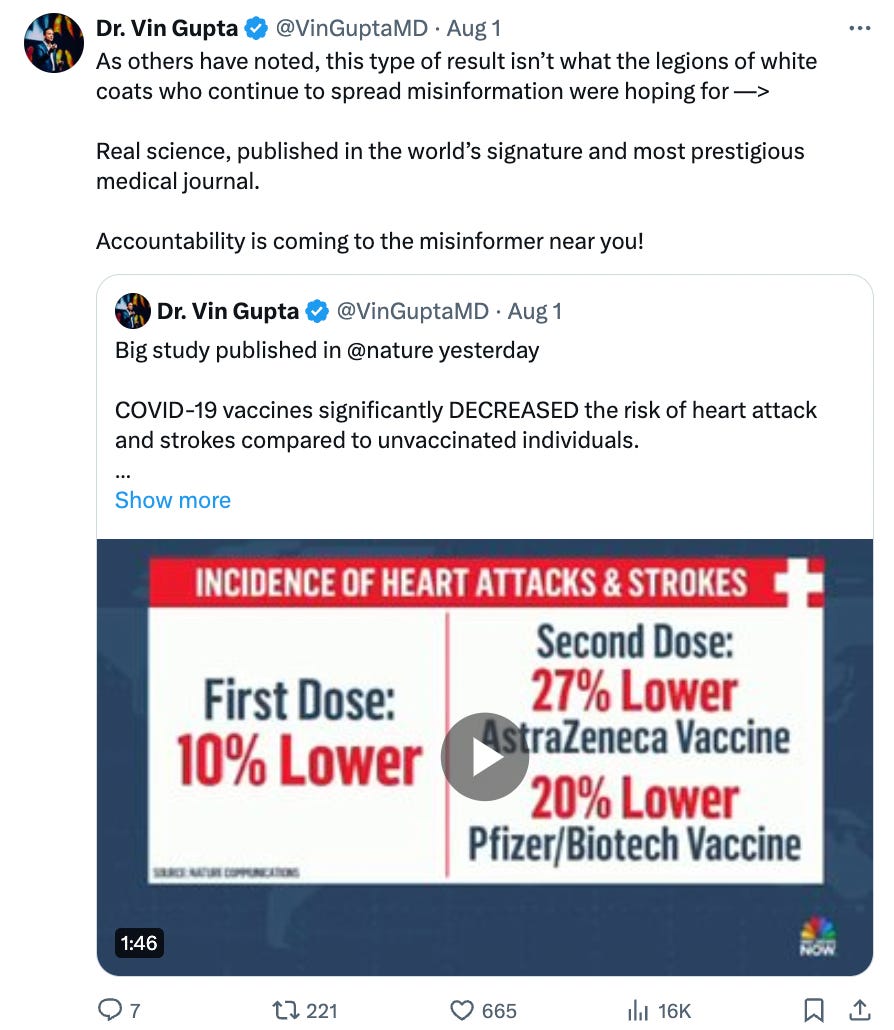
Problem 4: The news media is full of doctors who are not good at reading the literature. Here is Vin Gupta.
Literally no scientist thinks Nature COMMUNICATIONS is the most prestigious journal! Maybe some would say Nature, but not nature communications.
I wonder how Vin could have gotten that wrong, then I pubmed’ed him and see he doesn’t actually do much science, so he probably doesn’t know. He also doesn’t know how to read the paper.
Problem 5: It is odd that the authors find that dose after dose lowers cardiovascular events more, when most other data shows the first dose has the biggest impact on COVID19 complications.
“After second and booster vaccine doses, the reduction in incidence of composite arterial thrombosis was greater than after first vaccination. For example, aHRs for arterial thrombotic events 13–24 weeks after first vaccine dose were 0.99 (95% CI 0.97–1.02) after ChAdOx1 and 0.90 (0.88–0.93) after BNT-162b2. Corresponding aHRs after second doses were 0.73 (0.70–0.76) and 0.80 (0.77–0.83) respectively. aHRs for mRNA booster vaccination after primary course of ChAdOx1 were 0.71 (0.66–0.76) 13–24 weeks after BNT-162b2 and 0.67 (0.62–0.72) 5–24 weeks after mRNA-1273 respectively. [emphasis mine] ”
My first thought was that this reflects greater confounding— like repeat customers are even richer and better off— but my second thought was that the first dose actually had the worst CV harms, which offset the massive confounding problem. And each subsequent dose has less harms, so you see the confounding more. But no matter what is going on, the only way to know for sure would be to release way more falsification analyses. How much does each dose lower car accidents for e.g.?
Finally, whenever I breakdown a study, people comment that the authors are malicious— they are doing this on purpose—, There is an old saying “Never attribute to malice what can be explained by incompetence.”
Yes, absolutely there is a HUGE BIAS in medicine to DOWNPLAY covid19 vaccine risks and pretend we didn’t harm many young men with myocarditis, and everyone is incentivized to do that, from the FDA on downwards. But never underestimate how incompetent people are who do observational research, even those who have made a career out of it. And never ever underestimate just how incompetent doctors are who are correspondents for MSNBC. But yeah, no one wants to know about vaccine side effects after they forced hundreds of millions to get the shot that couldn’t halt transmission.










Never underestimate just how incompetent ANY correspondents for MSNBC are.
There are several levels of immorality to such bad science, including
1. The authors are likely aware of the flaws of their study, yet go forward seeking publication anyway, so this is the immorality of deception -- pretending they are bringing forth good science when they know they are not.
2. The editors are authorizing publication of bad science, knowing it is poorly done, indicating that they are corrupt and knowingly failing to do their job.
3. Those who ally with science journals are quick to call out those who publish, produce or cite quality science as "conspiracy theorists" or "spreaders of misinformation". Nonetheless, they are willing to reference poor science such as is seen in this study. This is the immorality of hypocrisy.
4. While those involved in publishing science may conceive their roles as disseminators of science, in fact the lives of many people hang in the balance of whether the science backs up medical products as safe and effective or not. Knowing their studies are of poor quality, it is reasonable to expect that they are contributing to the unnecessary sickening or killing of innocent people whose doctors relied on the science being published. This is the immorality of complicity with the crime of murder or assault and battery.
5. Many of those involved in the dissemination of bad science are probably motivated by the four B's: bullying, bribery, blackmail and bullshitting, by powerful interest groups. The failure to blow the whistle on these criminal activities consists of yet another crime of complicity -- allowing immoral at best and illegal at worst activities to taint the information field.
The people behind this pseudo-science, which has been outed by many great physicians, Marcia Angell and Richard Horton among them, may seem to be just unfortunate. It is not. It is a crime and should be prosecuted as one. The ethics underlying science and medicine has been thrown to the dogs. We need honest souls such as Dr. Prasad, Dr. McCullough, Dr. Cole, Dr. Malone, Dr. Kory, and many others to keep morality alive in what used to be a noble profession.